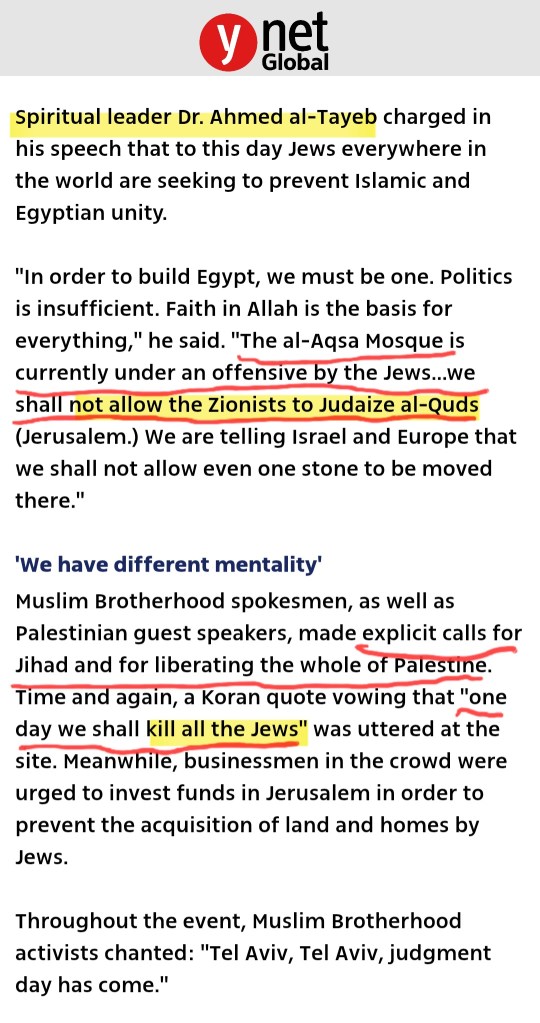
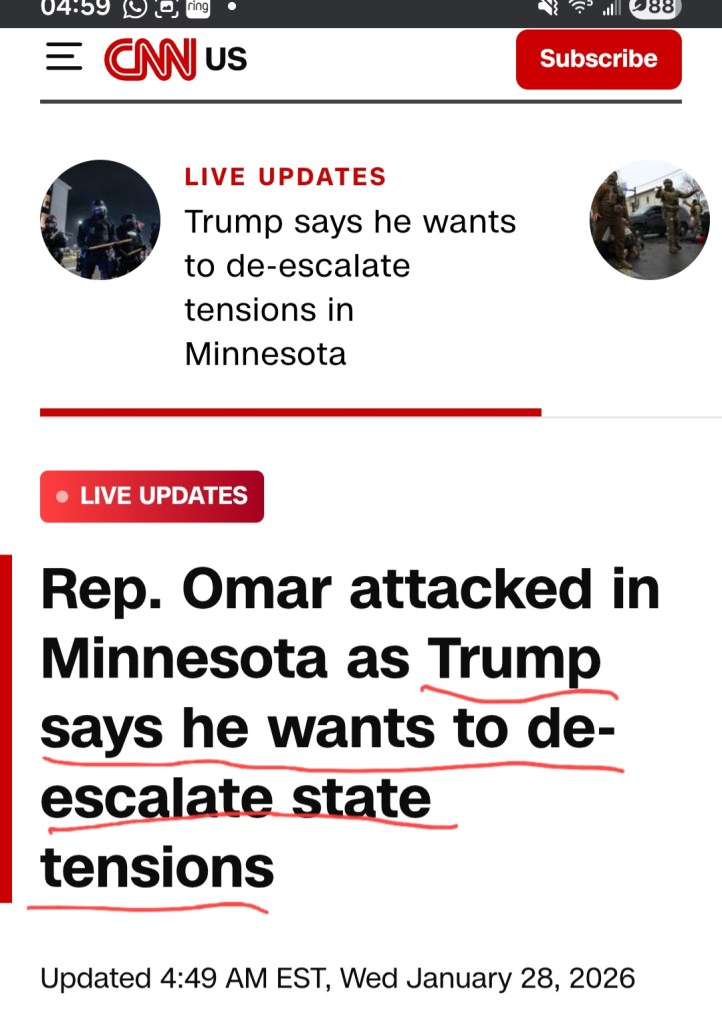
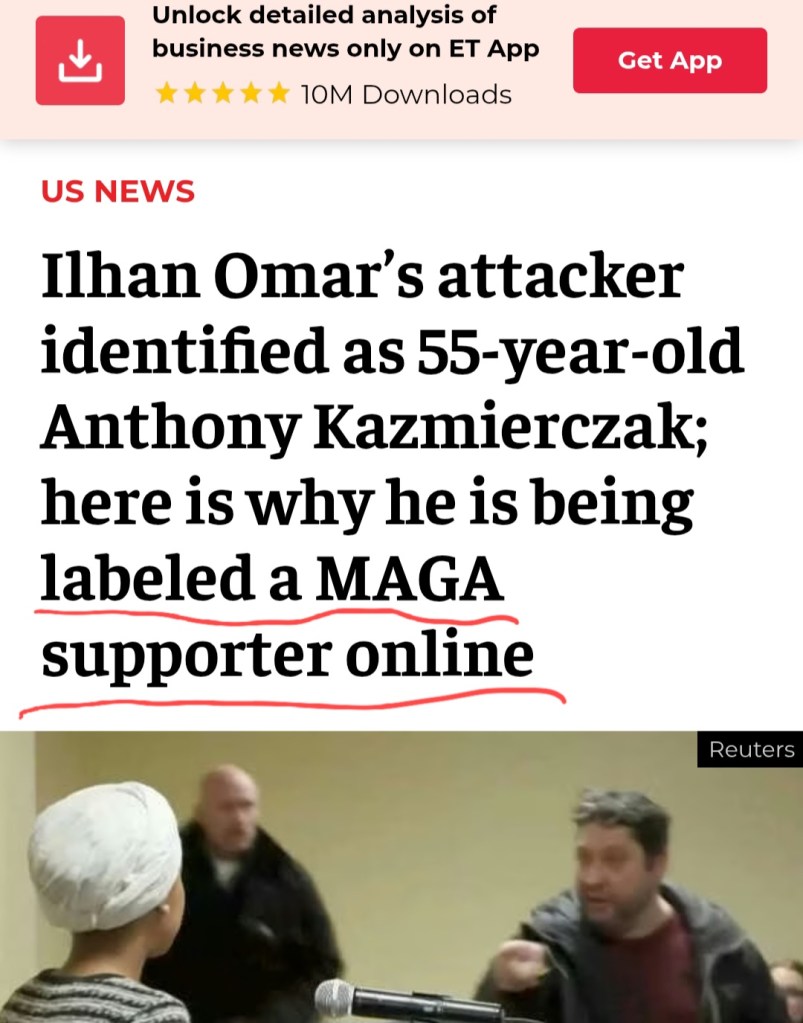
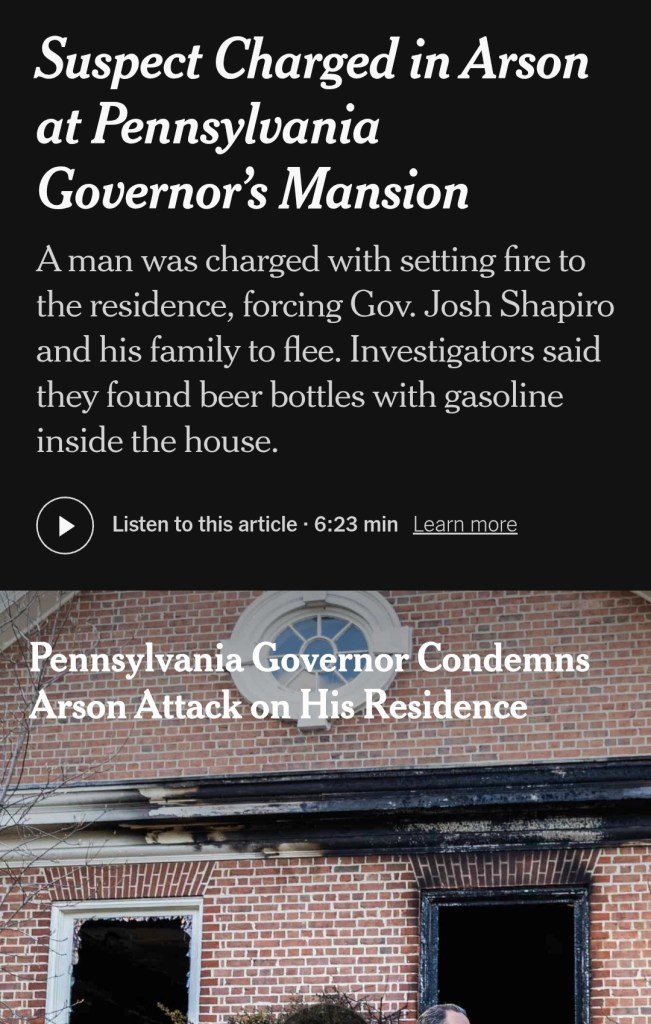
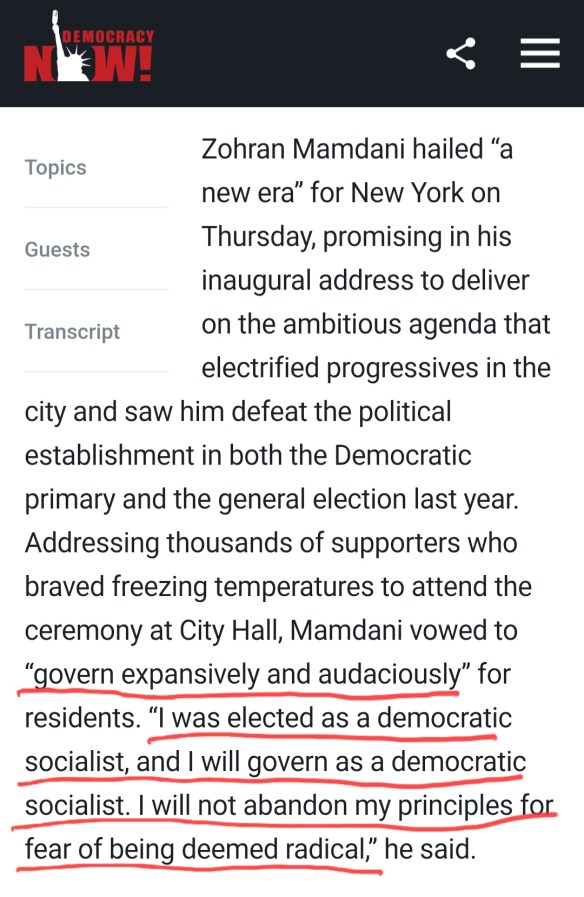
António Guterres keeps saying the United Nations is no longer the institution it was 80 years ago. Power must be rebalanced he claims. The Security Council must reflect today’s world he urges. Post–World War II structures must evolve.
Fine. But if that claim is serious, the UN’s most glaring failure to modernize is Gaza.
The system built never to end
One UN body remains frozen in 1948: UNRWA. One vision for a state is lost to contours proposed in 1947: Palestine.
“The world of 2026 is not the world of 1946.” – UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres, January 17, 2026
UNRWA administers a refugee regime found nowhere else:
- Refugee status is inherited indefinitely
- It never expires through citizenship or resettlement
- It is tied to a “right of return” not to Gaza or a future Palestinian state, but to Israel itself
No other refugee population is treated this way.
Bosnians were not. Syrians are not. Ukrainians are not.
Every other refugee crisis is handled by UNHCR, where refugee status is temporary and meant to end. Only Palestinians are placed in a system designed to remain permanent.
Ending inherited refugee status would not end humanitarian aid.
It would end the political weaponization of refugeehood.
Why Bosnia exposes the category error
After the Balkan wars, the Dayton Accords included a right of return—but it was finite, individual, and intra-state. It applied to homes lost in the same war for the same people, and aimed to undo ethnic cleansing, not undo borders.
Gaza’s claimed “right of return” is fundamentally different: intergenerational, extra-territorial, and demographic—designed to reopen 1948 and negate another UN member state.
Guterres’ contradiction
Guterres calls for reform everywhere except where reform would actually make peace possible.

As long as the UN maintains an inherited right of return into Israel and the proposed borders which have long since past their expiry:
- Maximalism is rewarded
- Compromise is delegitimized
- Negotiations become theater
- Gaza remains permanently “temporary”
This is not neutrality; it is an institutional choice to preserve claims that prevent settlement.
Reform that applies everywhere except where it matters most is not reform.
It is avoidance.
The unavoidable conclusion
Until the UN ends the one system designed never to end, Gaza will not be governed toward peace—but toward the permanence of conflict.
And no amount of rhetoric about modernization can disguise that refusal.